THE CARE TOOL
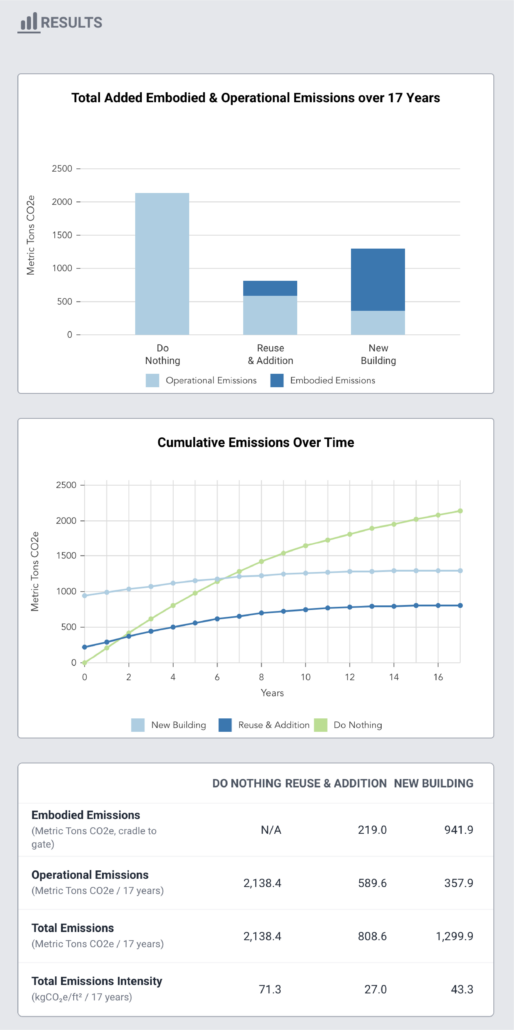
The CARE (Carbon Avoided: Retrofit Estimator) Tool is used for calculating and comparing the embodied, operating and avoided carbon impacts and benefits of reusing and upgrading existing buildings or replacing them with new construction.